Understanding Consumer Cohorts in XR
- Arnav Neel Ghosh

- May 8, 2024
- 7 min read
Updated: May 16, 2024
Expert Insight Series #1
Written By: Arnav Neel Ghosh
The adoption and usage of extended reality (XR) technologies, which encompass virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), is influenced by different consumer cohorts. Understanding the characteristics, preferences, and behaviors of these cohorts is crucial for businesses and developers to effectively design, market, and distribute XR experiences. This document provides an overview of the key consumer cohorts in the XR ecosystem, their unique traits, and the implications for the industry.
The factors driving growth
As the extended reality (XR) market continues to mature and evolve, the dynamics of consumer segmentation are also undergoing a transformative shift. What was once a relatively niche and tech-savvy early adopter landscape is now witnessing the emergence of diverse consumer cohorts, each with their unique preferences, behaviors, and expectations.
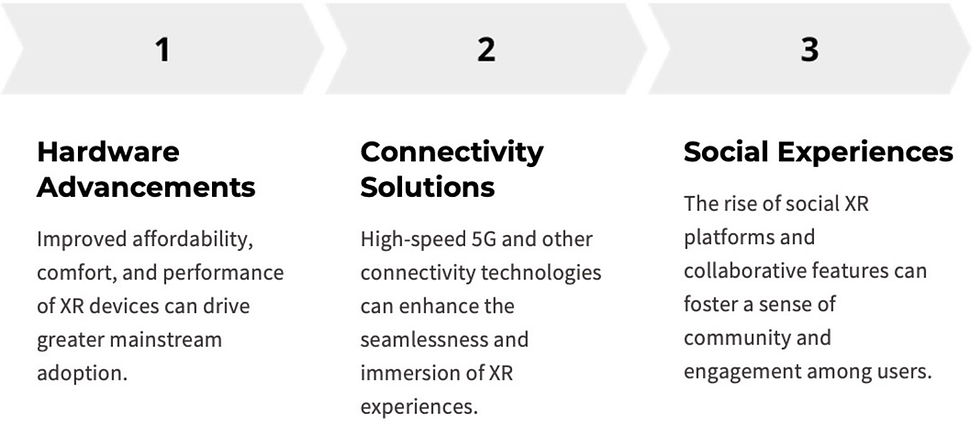
This evolution of consumer segments is crucial for businesses and developers to understand, as it shapes the strategic direction, product design, and go-to-market strategies for XR technologies. There are three critical drivers of change.
Key evolving Personas
As the XR industry continues to evolve, the personas and user profiles that define key consumer cohorts are also undergoing a dynamic transformation. The traditional early adopter, mainstream consumer, and enterprise user archetypes are becoming increasingly nuanced, with emerging sub-segments and blurred boundaries. This evolution is driven by factors listed above such as advancements in hardware, the growing emphasis on social and collaborative experiences, and the increasing diversity and accessibility of XR technologies.
For example, the early adopter persona is no longer solely defined by their technical prowess and thirst for novelty. As XR devices become more user-friendly and affordable, a new generation of "tech-savvy enthusiasts" is emerging - individuals who are drawn to the immersive and experiential aspects of XR, rather than just the underlying technology. These consumers may be less inclined to tinker with complex setups, but they are eager to explore the creative and social possibilities of XR in their daily lives.
The evolution of these personas underscores the need for businesses and developers to continuously refine their understanding of XR consumers, their motivations, and their evolving needs. By staying attuned to these shifts, organizations can tailor their XR offerings, marketing strategies, and user experiences to better resonate with the diverse and dynamic landscape of XR users. This dynamic approach will be crucial in driving widespread adoption and ensuring the long-term success of the XR industry.
Early Adopters: Tech-Savvy Enthusiasts
The early adopter cohort in the XR space is typically composed of tech-savvy individuals who are eager to embrace the latest advancements in immersive technologies. These consumers are often tech enthusiasts, gadget lovers, and early adopters of new consumer electronics. They are driven by a desire to explore the cutting-edge capabilities of VR, AR, and MR, and they are willing to invest time and resources to understand and integrate these technologies into their daily lives.
Early adopters are highly influential within their social circles and online communities, and their feedback and recommendations can significantly impact the broader market adoption of XR technologies. Businesses targeting this cohort should focus on highlighting the innovative features, cutting-edge capabilities, and the sense of novelty and exclusivity associated with their XR offerings.
Curiosity
Early adopters are driven by a strong curiosity to explore and understand new technologies, often seeking out the latest XR hardware and software.
Early Adoption
They are willing to be among the first to try and adopt XR technologies, even when the
experiences and devices may not be fully polished or
mainstream-ready.
Influencing Adoption
Early adopters often serve as evangelists, sharing their experiences and recommendations within their social networks, which can significantly impact the broader adoption of XR technologies.
Mainstream Consumers: Entertainment and Social Experiences
As XR technologies mature and become more accessible, the mainstream consumer cohort is expected to play a pivotal role in driving mass-market adoption. This cohort is primarily interested in using XR for entertainment and social experiences, such as gaming, virtual concerts, and social networking platforms.
Mainstream consumers are typically less tech-savvy than early adopters and are more focused on the practical applications and user-friendly experiences of XR. They want to be able to seamlessly integrate XR into their daily lives, whether it's for gaming, socializing, or consuming media. Businesses targeting this cohort should prioritize developing intuitive and polished XR experiences that are accessible, affordable, and offer compelling content and social features.
Gaming
Mainstream consumers are drawn to immersive gaming experiences that offer a sense of escapism and social interaction. VR and AR- enabled games that provide high-quality graphics, intuitive controls, and opportunities for multiplayer engagement are likely to resonate with this cohort.
Social Experiences
Mainstream consumers are interested in using XR for virtual social gatherings, such as virtual concerts, meetups, and collaborative workspaces. Platforms that enable seamless social interaction and communication in immersive environments will be particularly appealing.
Media Consumption
Mainstream consumers are also interested in using XR for consuming media, such as watching movies, TV shows, and live events in a more immersive and engaging way. XR- enabled content platforms that provide high-quality, user- friendly experiences will be well-received by this cohort.
Enterprise Users: Productivity& Collaboration
The enterprise user cohort represents a significant and growing segment of the XR market, as businesses recognize the potential of these technologies to enhance productivity, collaboration, and training within their organizations. Enterprise users are primarily interested in using XR for practical applications, such as remote collaboration, 3D visualization, and hands-on training and simulation.
Businesses targeting the enterprise user cohort should focus on developing XR solutions that address specific industry challenges, integrate seamlessly with existing workflows and enterprise software, and provide measurable improvements in efficiency, productivity, and cost savings. Robust security, scalability, and enterprise-grade support are also crucial considerations for this cohort.
Remote Collaboration
XR technologies enable enterprise users to collaborate in virtual workspaces, allowing for more effective communication, data sharing, and task coordination across distributed teams.
Visualization and Simulation
XR-based visualizations and simulations can greatly enhance decision-making, product development, and training processes by providing immersive, 3D representations of complex data and scenarios
Hands-on Training
XR-enabled training programs can offer a safe, cost-effective, and scalable way for enterprise users to acquire new skills and practice critical tasks in a realistic, virtual environment.
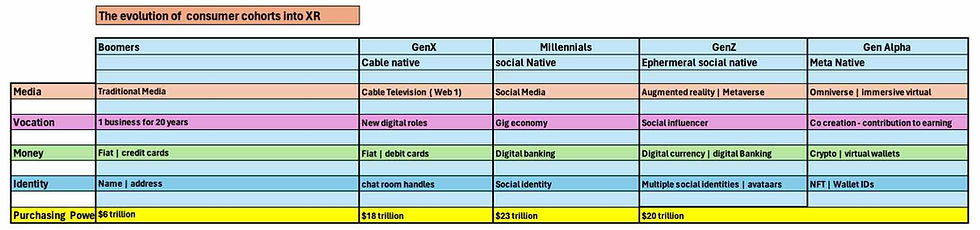
Demographic Shifts: Age |Gender | Income
The adoption and usage of XR technologies are influenced by demographic factors, such as age, gender, and income level. As the XR market continues to evolve, businesses must consider these shifting demographic trends to effectively target and engage the various consumer cohorts.
For example, younger consumers, particularly those in the Gen Z and Millennial age groups, have shown a higher propensity for adopting and engaging with XR technologies, often driven by their familiarity with digital media and a desire for immersive experiences. On the other hand, older consumers may require more accessible and user- friendly XR solutions to overcome potential barriers, such as technological literacy and physical limitations.
Gender also plays a role in XR adoption, with research indicating that men are more likely to be early adopters of XR technologies compared to women. However, as the market matures and XR experiences become more diverse and inclusive, the gender gap is expected to narrow. Income level is another factor, as higher-income consumers are more likely to have the resources to invest in premium XR hardware and content.

Regional Variations: Global XR Adoption Patterns
The adoption and usage of XR technologies vary significantly across different regions and countries worldwide. Understanding these regional variations is crucial for businesses and developers looking to expand their XR offerings globally.
For instance, certain regions, such as North America and East Asia, have historically been more receptive to and invested in the development of XR technologies, leading to higher adoption rates and a more mature ecosystem. On the other hand, other regions, such as parts of Africa and South America, have experienced slower XR adoption due to factors such as limited infrastructure, economic constraints, and lower technological literacy.
Factors like cultural preferences, regulatory environments, and the availability of supporting technologies (e.g., high-speed internet, compatible devices) can also influence the pace and patterns of XR adoption in different regions. Businesses seeking to expand their XR offerings globally must carefully analyze these regional dynamics and tailor their strategies accordingly to ensure successful market penetration and long-term growth.
North America and East Asia
These regions have been at the forefront of XR adoption, with a more mature ecosystem, higher consumer demand, and significant investment in XR technologies.
Emerging Markets
Regions like Africa, South America, and parts of Asia are experiencing slower XR adoption due to factors such as limited infrastructure, economic constraints, and lower technological literacy
Regional Factors
Cultural preferences, regulatory environments, and the availability of supporting technologies can all influence the pace and patterns of XR adoption in different regions around the world.
Barriers to Mass Market Adoption
Despite the growing popularity and potential of XR technologies, several barriers and challenges remain that hinder the achievement of mass-market adoption. These barriers must be addressed by businesses, developers, and policymakers to unlock the full potential of XR and drive widespread consumer engagement.
One of the primary barriers is the high cost of XR hardware, which can limit accessibility and affordability, particularly for mainstream consumers. Additionally, the complexity and technical know-how required to set up and use XR systems can be intimidating for some users, creating a barrier to entry. Concerns about privacy, data security, and potential health and safety risks associated with prolonged XR use are also factors that can deter consumer adoption.
Addressing these barriers will require a multi-faceted approach, including technological advancements to improve affordability and ease of use, as well as educational initiatives and policy measures to address regulatory and safety concerns. By overcoming these challenges, businesses can pave the way for XR technologies to become truly mainstream and accessible to a wide range of consumers.

Summing up the key factors which will help define consumer segments | broaden narratives and create more focused consumption opportunities
As the extended reality(XR) market continues to evolve, several emerging trends and developments are poised to shape the future of this rapidly changing landscape. These trends hold the potential to drive increased consumer adoption, enhance user experiences, and unlock new applications and use cases for XR technologies. One prominent trend is the ongoing advancements in XR hardware. Manufacturers are developing more lightweight, comfortable, and affordable XR devices, such as virtual reality (VR) headsets and augmented reality (AR) glasses.
These improvements in hardware design and affordability can make XR technologies more accessible to mainstream consumers, driving greater adoption and engagement. Additionally, the integration of 5G and other high-speed connectivity solutions can enable more seamless and immersive XR experiences, reducing latency and enhancing the overall user experience.
Another key trend is the growing emphasis on social and collaborative XR experiences. As consumers seek more engaging and interconnected ways to interact with each other in virtual environments, the development of social XR platforms and the integration of features like multi-user experiences, virtual avatars, and shared virtual spaces can foster a sense of community and social connection among XR users. These advancements can transform the way people work, learn, and socialize in the digital realm.





Comments